Celastrol is a natural compound isolated from the root extracts of Tripterygium wilfordii (Thunder god vine). Together with artemisinin, triptolide, capsaicin and curcumin, it has been listed by Cell journal as one of the five Traditional Chinese Medicines most likely to be developed into modern drugs (Corson T. W and Crews C. M., Cell, 2007). It has anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-cancer, neuroprotective, and anti-obesity effects, but its specific molecular mechanisms of action, especially anti-cancer, are still unclear.
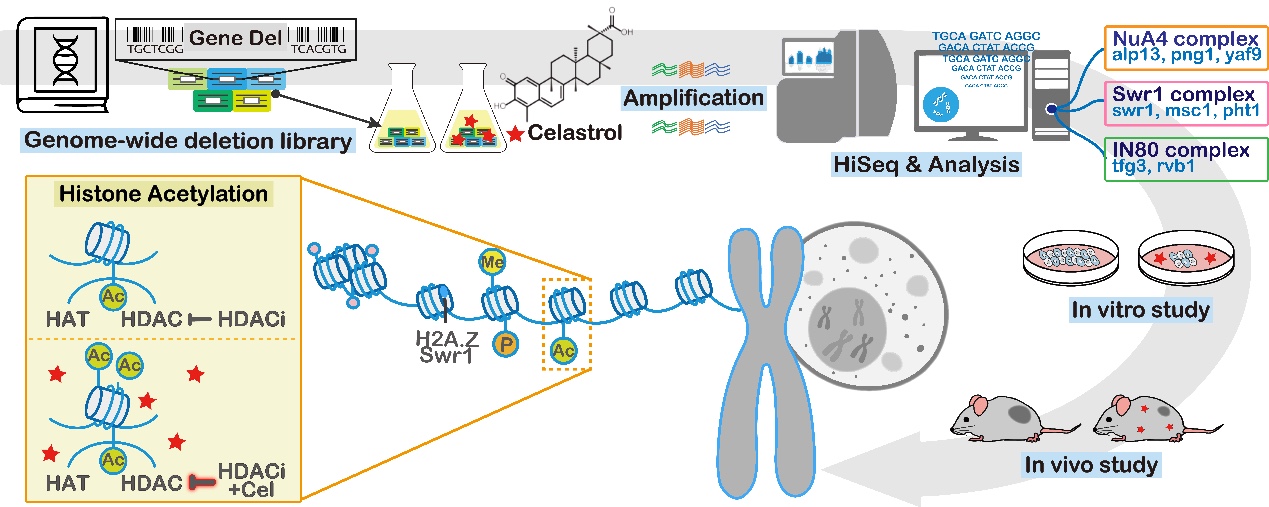
Dr. Neher’s Biophysics Laboratory for Innovative Drug Discovery used a molecular barcoded eukaryotic genome-wide gene deletion library to investigate the anticancer mechanism of celastrol at the genomic level. Through chemical genomics and bioinformatics analysis, researchers found that the genes associated with the action of celastrol are specifically focused on histone modification and remodeling, a biological process in which celastrol can affect histone acetylation, methylation and phosphorylation modifications. Among the papers on celastrol, this study revealed the mechanism of histone modification by celastrol is the first to be reported. The discovery of this mechanism unifies the existing anticancer mechanisms of celastrol, such as inhibiting cell proliferation and inducing apoptosis and autophagy at the level of gene regulation. The researchers also found that combining celastrol and HDACi (histone deacetylase inhibitor) significantly inhibited lung cancer cell proliferation and tumor growth. The inhibitory effect was superior to that of the drug alone. This finding also provides a significant reference value for lung cancer treatment research.
The related research article was published in the journal Pharmacological Research (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106487). Assistant Professor Lijuan Ma and Haijie Yu are the corresponding authors of the article, and Master's students Geer Chen and Xiaoyu Zhu are the first authors of the article.
The anticancer mechanism of celastrol through modulation of histone modifications
