The Faculty of Medicine of M.U.S.T. highlights AI’s important role
in diagnosis and prognosis of COVID19 pneumonia in international top journal Cell
Since the COVID-19 pneumonia (also called as NCP) outbreak, the medical community has been working together both domestically and overseas, effectively controlling the national outbreak. However, the pandemic prevention and control overseas still represents a major health threat. According to the world health organization (WHO) statistics, as of April 26 there are 2,897,645 confirmed cases worldwide, 202,880 fatal cases and the virus reached more than 200 countries and regions. The global NCP outbreak has been classified by the WHO as the highest level of public health emergency.
On April 25, Professor Kang Zhang of the Faculty of Medicine of M.U.S.T. published a groundbreaking work in the top international journal 《Cell》,entitled "Clinically Applicable AI System for Accurate Diagnosis, policy Measurements and Prognosis of COVID - 19 root Using Computed Tomography" as the first author and corresponding author, and M.U.S.T. as the first affiliated organization coinciding with the University’s debut on 《Cell》.《Cell》 is a peer-reviewed scientific journal publishing research papers across a broad range of disciplines within the life sciences.
The Dean of the Faculty of Medicine of M.U.S.T., Dr. Fok said, “Prof. Zhang’s team in cooperation with Tsinghua University and Sun Yat-Sen Memorial Hospital of Sun Yat-Sen University, joint with the Guangzhou Regenerative Medicine and Health Guangdong Laboratory, West China Hospital of Sichuan University and other institutions, developed an AI-assisted diagnostic system for COVID-19 pneumonia based on CT images. The system can efficiently distinguish NCP from OVP (other viral pneumonia) and predict the severity level in 20 seconds, and the accuracy is up to 90% and above. NCP not only causes the symptoms such as fever, cough, fatigue, but can also affect a variety of tissue and organ systems, and develop to severe acute respiratory distress syndrome. Prognosis is poor, and mortality is high. Therefore, identifying risk factors and generating predictive models is critical for early intervention and better outcomes.”
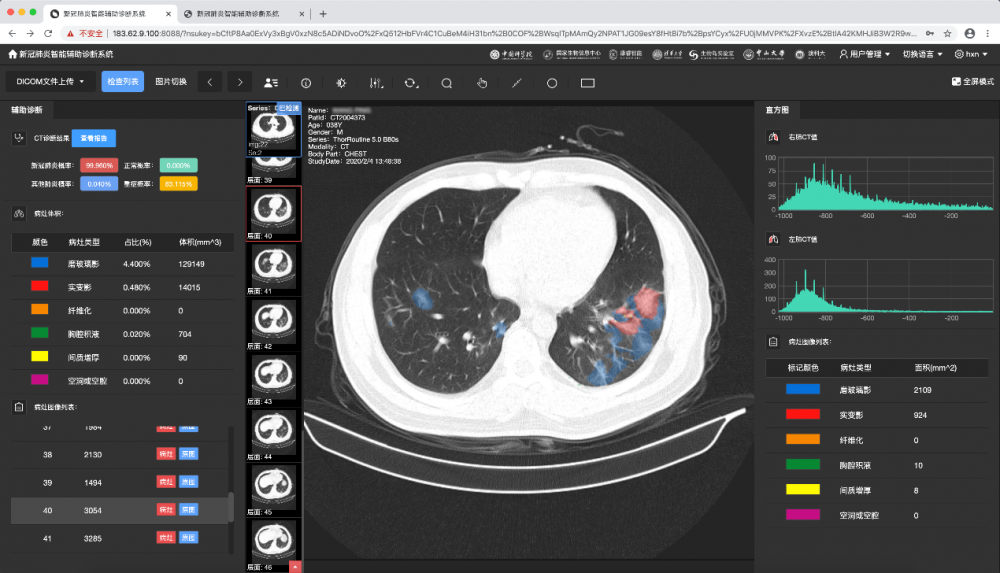
AI-assisted diagnostic system for COVID-19 Pneumonia based on CT images
According to Prof. Zhang, the study used one of the largest CT dataset in the world with more than 500,000 CT images. The AI team uses deep learning, semantic segmentation and multiple neural network architectures to create an accurate AI diagnostic system. Texture analysis was performed to distinguish NCP from OVP. The lung lesions after the segmentation were quantitatively measured, such as the volume ratio of ground glass and solid volume ratio. In addition, based on the international standard on related research of lung lesions, lung, liver damage and clinical indicators, they developed a comprehensive rating system. The system can accurately project NCP severe lesions, which is a valuable contribution to the intervention and treatment outcome, especially in the course of contrast of lesions and the clinical drug use guide. The technology advances the development of precision medicine, AI medicine and longitudinal follow-up. It also suggests a new prevention approach that, in addition to improving lung function, protecting other vital organs and the cycling characteristics of stable systems can prevent progression to critical diseases.
With the advantages of high precision and high efficiency, the AI model can not only assist clinicians’ decisions on diagnosis, improve diagnostic accuracy, relieve the need for diagnostic expertise, but also reduce their workload, accelerate diagnostic efficiency, and decrease patients' waiting time. It provides an effective basis for disease progression and prognosis management. With the release of the paper, a high-quality and large-scale imaging database is also available and technical code is shared with the world. This represents a breakthrough in technology and makes a great contribution to international research on COVID-19 Pneumonia. At the same time, the AI-assisted diagnostic system has been improved after multiple algorithm and system upgrades, now featuring a bilingual version. Several pilot hospitals are have been deployed, and the system is getting high recognition from a lot of areas.





