Immune checkpoint inhibitors are currently the most common tumor immunotherapy used in the clinical treatment of melanoma, breast cancer, bladder cancer, lung cancer, and many other cancers. However, due to the complex tumor microenvironment, patients with non-small cell lung cancer have a low response rate to immune checkpoint inhibitors, and their survival rate is not significantly improved. PD-L1, carried by extracellular vesicles (exosomes) secreted by tumor cells, is an important cause of PD-L1/PD-1 inhibitor resistance.
Recently, Dr. Haijie Yu from Dr. Erwin Neher's Biophysics and Innovative Medicines Laboratory at Macau University of Science and Technology (M.U.S.T.), in collaboration with Nobel Laureate Prof. Erwin Neher himself, published a paper entitled "Suppression of PD-L1 release from small extracellular vesicles promotes systemic anti-tumor immunity by targeting ORAI1 calcium channels" in the Journal of Extracellular Vesicles (IF:17.3, Journal of Extracellular Vesicles, 11,e12279. https://doi.org/10.1002/jev2.12279). The study found that in lung cancer cells, the calcium channel protein ORAI1 can influence the release of exosomal PD-L1 through intracellular calcium signaling. The authors first found that increased intracellular calcium concentration promoted exosomal PD-L1 release. Knocking down ORAI1, a calcium channel protein that affects intracellular calcium concentration, inhibited exosomal PD-L1 release in non-small cell lung cancer. Knockdown of ORAI1 in mouse lung cancer cells also inhibited exosomal PD-L1 release and delayed tumor progression in a mouse lung cancer model. The authors evaluated the function of immune cells and found that immune cell activity was enhanced, and infiltration in the tumor was increased in the ORAI1 knockdown tumor model. The authors further found that calcium ions regulate the release of PD-L1 from tumor cells mainly through the MLPH and SLP2-a proteins. Therefore, ORAI1 calcium channels are closely related to tumor immunity and could be a new target for anticancer action.

From right: Assistant Professor Haijie Yu and Chen Xi.
Dr. Yu’s group in Dr. Erwin Neher's Biophysics and Innovative Medicines Laboratory focuses on ion channels and complex diseases, such as tumors. Xi Chen, a Ph.D. student who graduated from Dr. Yu’s group is the paper's first author. Prof. Vincent Kam-Wai Wong and Adjunct Chair Prof. Liang Liu are co-corresponding authors, and Dr. Lijuan Ma also participated in the work. This research was supported by the Faculty Research Grant Projects of Macau University of Science and Technology (FRG-18-002-SK & FRG-18-003-SK) and the Macao Science and Technology Development Fund (Project No. 0020/2019/A1, 0062/2021/A2 & 001/2020/ALC to E.N & H.Y).
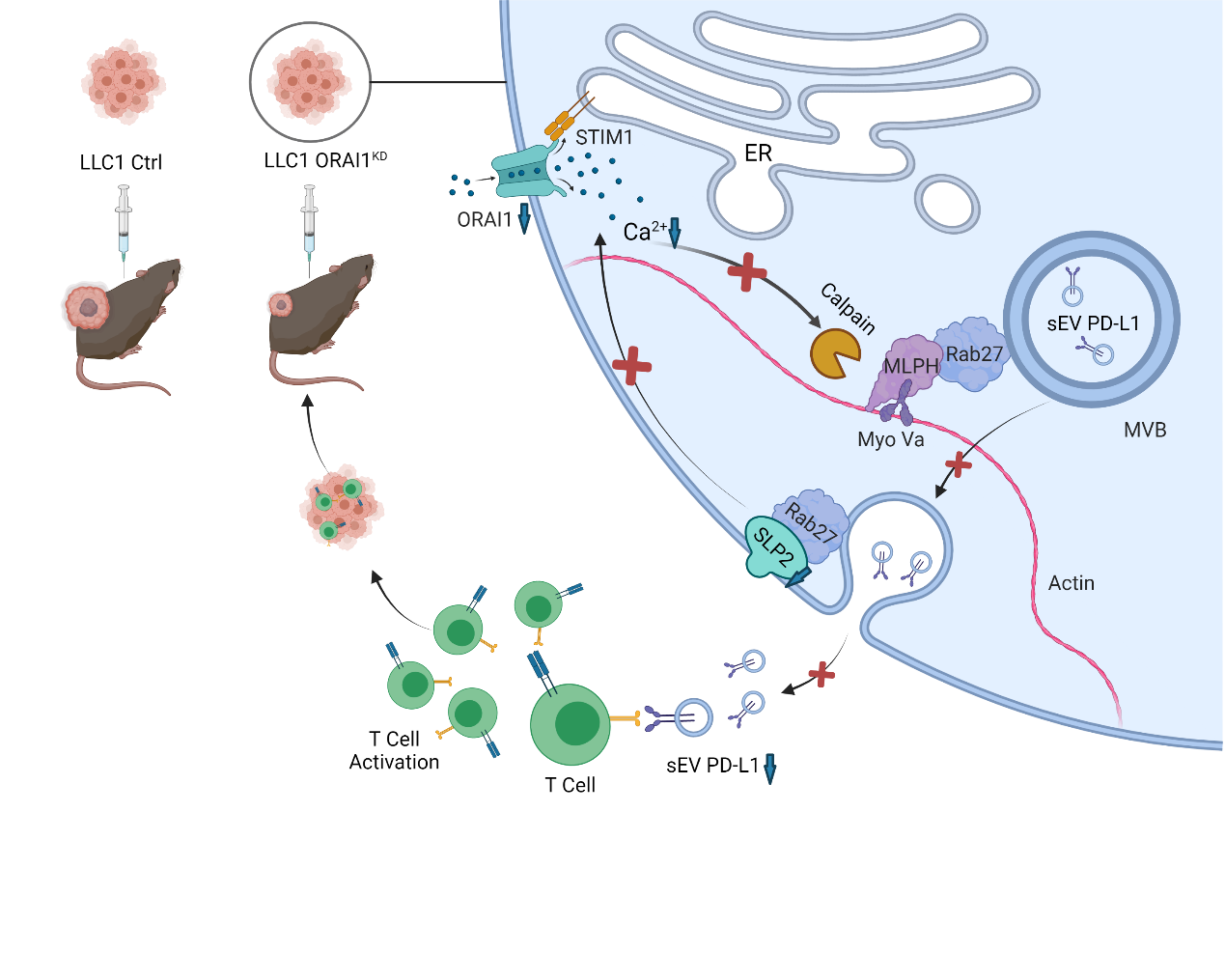
ORAI1 calcium channel regulates exosomal PD-L1 release in lung cancer cells and remodels anti-tumor immunity to suppress the tumor growth
 Immune checkpoint inhibitors are currently the most common tumor immunotherapy used in the clinical treatment of melanoma, breast cancer, bladder cancer, lung cancer, and many other cancers. However, due to the complex tumor microenvironment, patients with non-small cell lung cancer have a low response rate to immune checkpoint inhibitors, and their survival rate is not significantly improved. PD-L1, carried by extracellular vesicles (exosomes) secreted by tumor cells, is an important cause of PD-L1/PD-1 inhibitor resistance.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors are currently the most common tumor immunotherapy used in the clinical treatment of melanoma, breast cancer, bladder cancer, lung cancer, and many other cancers. However, due to the complex tumor microenvironment, patients with non-small cell lung cancer have a low response rate to immune checkpoint inhibitors, and their survival rate is not significantly improved. PD-L1, carried by extracellular vesicles (exosomes) secreted by tumor cells, is an important cause of PD-L1/PD-1 inhibitor resistance.